Let's assume you've read all of VMware's recommended reference books on how to design a vSAN platform. You've designed the fabric of your vSAN for traffic management. You've calculated your vSAN's storage requirements for its Capacity Layer and its Cache Layer. What's next?
You can follow this simplified guide with only seven steps to get your vSAN working!
Step #1
Assemble your servers with the correct ratios of disk drives to flash drives.
Step #2
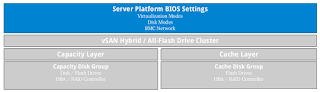
Configure the BIOS settings of your servers.
Step #3
Install the ESXi software on your servers. ESXi will automatically configure itself based on the BIOS settings.
Step #4
Check that the vSAN objects were setup correctly on your servers.
Step #5
Install the vCSA software on a server outside of your storage cluster, then configure your Organization, Primary Adapter, and Primary Virtual Switch.
Step #6
Connect to your vCSA using your vSphere client to configure virtual switches for Management Traffic, vSAN Traffic, and vMotion Traffic.
Step #7
Connect to your vCSA using your vSphere client to configure your vSAN's storage policy.
Conclusion
That's it! Now you can start using your vSAN clustered storage. Let's take a look at what you engineered






Comments
Post a Comment
Comments to this blog will be reviewed within 72 hours. No trolling please